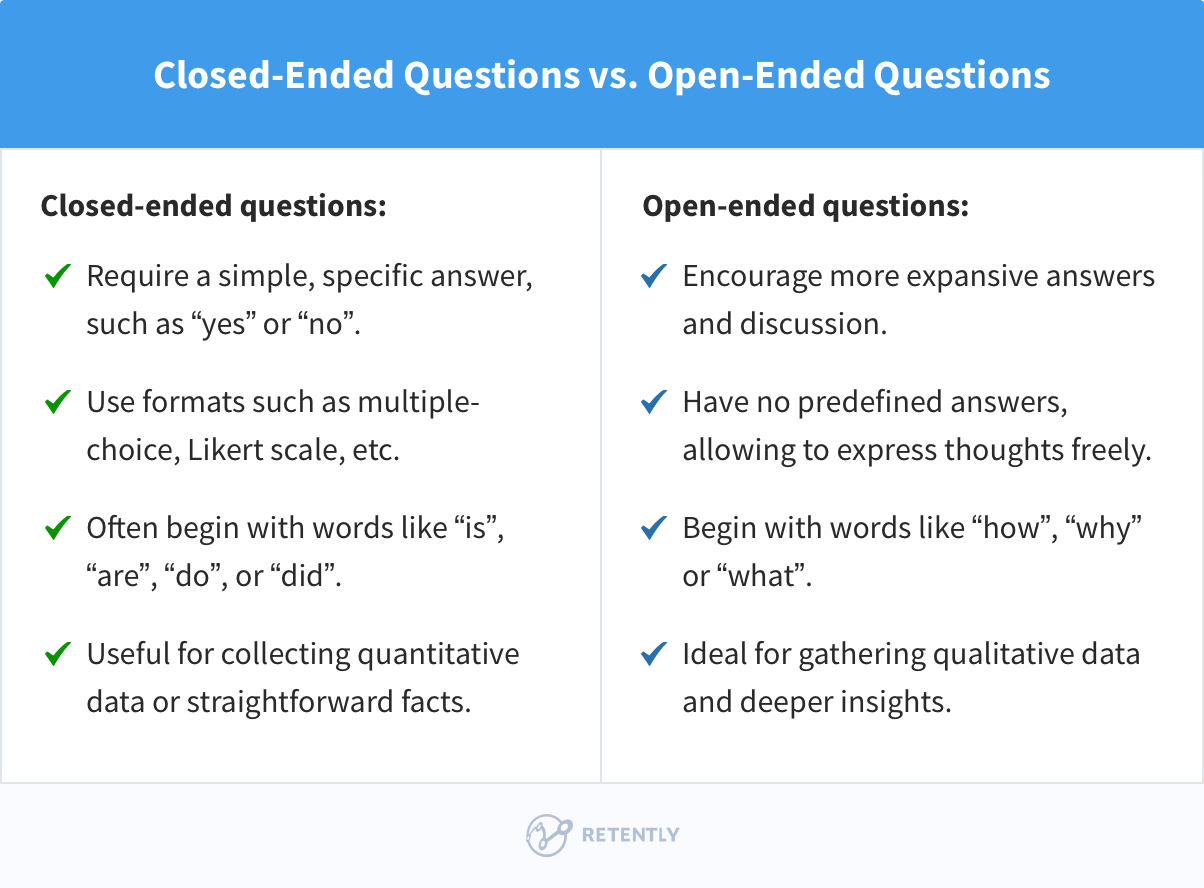
Open-ended survey questions serve as an invaluable tool for gathering qualitative data, offering respondents the opportunity to articulate their thoughts, feelings, and experiences in their own words. This format stands in stark contrast to closed-ended questions, which restrict answers to predefined options. By allowing for a more expansive response, open-ended queries can yield deeper insights and nuanced perspectives that can illuminate the complex landscape of participant attitudes and behaviors. Below, various examples of effective open-ended survey questions are presented, categorized by context and objective.
1. Product Feedback
To ascertain consumer sentiments about a product, open-ended questions can unearth valuable insights. For instance:
- “What features of our product do you find most beneficial, and why?” This question prompts respondents to reflect on specific functionalities, encouraging them to articulate not only what they appreciate but also the reasons behind their favorable impressions.
- “In what ways do you think our product could be improved?” A query framed this way invites candid criticism and suggestions, fostering a constructive dialogue that may enhance product development.
2. Customer Service Evaluation
Open-ended questions can be invaluable in assessing the quality of customer service. Consider the following examples:
- “Can you describe your recent experience with our customer service team?” This asks respondents to convey their experiences in detail, allowing for a comprehensive analysis of service quality.
- “What suggestions do you have for enhancing our customer service?” Such a query empowers customers to express their desires for improved service, thereby giving businesses actionable insights.
3. Event Feedback
Gathering feedback post-event is crucial for identifying strengths and areas for improvement. Examples include:
- “What did you enjoy most about the event, and what could we have done differently?” This dual-faceted question encourages respondents to highlight both positive aspects and opportunities for enhancement, providing a well-rounded perspective.
- “How did the event meet or fail to meet your expectations?” By inviting attendees to evaluate their expectations versus reality, insights can be gleaned about future event planning.
4. Employee Engagement
In organizational contexts, understanding employee sentiment is imperative. Open-ended inquiries can reveal the underlying morale. Examples include:
- “What motivates you to excel in your role?” This question probes into the intrinsic and extrinsic factors that drive employee performance, offering leaders insight into what truly engages their workforce.
- “What changes would you suggest to improve the workplace environment?” By soliciting suggestions, organizations can actively engage employees in the reform process, fostering a culture of collaboration.
5. Market Research
Open-ended questions hold significant value in market research by capturing consumer preferences and trends. Consider the following:
- “What brands do you associate with quality in our industry, and why?” This question invites respondents to reflect on brand perceptions and the qualities that contribute to a brand’s reputation, aiding in competitive analysis.
- “What factors influence your purchasing decisions?” By asking this, researchers can uncover the myriad influences that shape consumer behavior, from social proof to product features.
6. Social Issues Exploration
When delving into societal concerns, open-ended questions can uncover the complexities of public opinion. For example:
- “How do you feel about the current state of social justice initiatives?” Respondents can share their thoughts, feelings, and personal experiences, leading to a richer dialogue about societal challenges.
- “What changes do you believe are necessary to promote inclusivity in our community?” This encourages respondents to articulate actionable ideas, fostering community engagement and advocacy.
7. Academic Research
In academic settings, open-ended questions can lead to significant insights. Examples include:
- “How has your educational experience shaped your career aspirations?” This allows participants to narrate personal stories, contributing qualitative data that can enrich research findings.
- “What barriers to learning do you perceive in your educational journey?” Such questions can highlight systemic issues and personal challenges within the educational landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, open-ended survey questions are an essential instrument across a myriad of contexts, empowering respondents to express their views in an uninhibited manner. Their capacity to generate rich, qualitative insights is unparalleled, facilitating a deeper understanding of customer experiences, employee sentiments, and societal dynamics. When crafted thoughtfully, these questions transform ordinary surveys into profound dialogues, allowing organizations, researchers, and community leaders to glean invaluable insights that drive action and improvement. The versatility and depth of open-ended questions make them indispensable tools in the pursuit of knowledge and understanding.