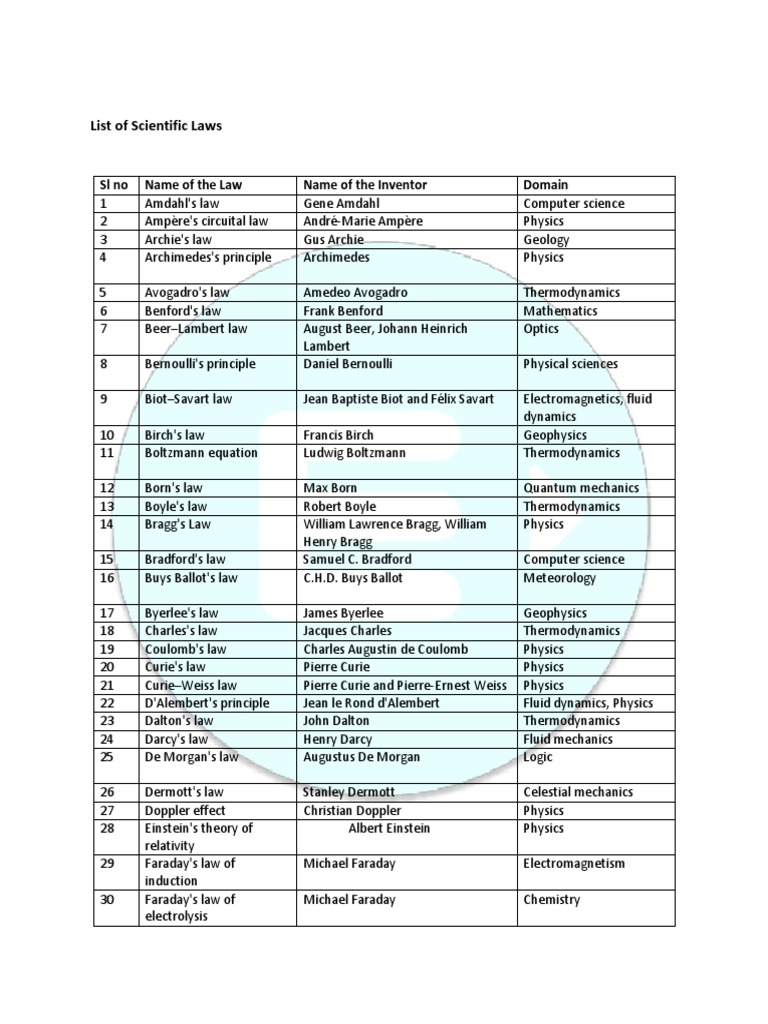
Scientific laws form the bedrock of our understanding of the natural universe. They encapsulate observations and principles that invariably hold true within specific conditions. Let us explore some exemplary scientific laws, elucidating their significance and implications across various fields of study.
Definition of a Scientific Law
A scientific law is a statement that describes an observable phenomenon, often articulated in mathematical terms or empirical relationships. Unlike theories, which offer explanations for why phenomena occur, laws describe what happens under certain conditions. This distinction is pivotal as it informs both students and scholars about the predictive power of various scientific assertions.
The Law of Gravity
One of the most universally recognized scientific laws is the Law of Gravity, formulated by Sir Isaac Newton in the late 17th century. This law states that every mass attracts every other mass in the universe with a force that is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. This remarkably straightforward yet profound principle explains everything from the falling of an apple from a tree to the staggering orbits of planets around the sun.
Gravity serves as a fundamental force that binds celestial bodies and governs the motion of planets, thereby shaping the very structure of the cosmos. It is essential in fields such as astrophysics and cosmology, which explore not only the movement of bodies but also the structure and evolution of the universe.
Law of Conservation of Mass
Next, we turn our attention to the Law of Conservation of Mass, articulated by Antoine Lavoisier in the late 18th century. This law posits that mass is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction; it is solely transformed. This principle is foundational in chemistry, underpinning stoichiometric calculations and balancing chemical equations.
The implications of this law extend beyond simple chemical interactions. In environmental science, it serves as a crucial tenet when discussing ecosystems and waste management. Understanding that matter is conserved allows scientists to assess and predict how pollutants interact within the environment, facilitating the development of effective strategies for pollution control and resource management.
Ohm’s Law
In the realm of electrical engineering, Ohm’s Law plays a vital role in determining the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance within electrical circuits. Stated simply, it asserts that the current passing through a conductor between two points is directly proportional to the voltage across the two points and inversely proportional to the resistance. Mathematically, this is expressed as V=IR, where V is the voltage, I is the current, and R is the resistance.
Ohm’s Law is indispensable in circuit design and analysis. It empowers engineers to predict how electrical systems will behave under varied conditions, serving as a critical tool in both educational settings and practical applications in electronics, telecommunications, and more.
Second Law of Thermodynamics
The Second Law of Thermodynamics introduces the concept of entropy, asserting that in any energy exchange, if no energy enters or leaves the system, the potential energy of the state will always be less than that of the initial state, indicating a natural tendency towards disorder. This law encompasses the idea of irreversibility, explaining why processes such as melting ice, burning wood, or mixing colored dyes always lead to greater entropy.
Its implications are vast, influencing disciplines ranging from chemistry and physics to biology and even cosmology. In biological systems, for instance, the Second Law helps in understanding energy transformations in metabolism and the sustainability of ecosystems. It underscores the intricate dance between order and chaos that pervades nature.
Conclusion
Scientific laws have an unparalleled ability to demystify the complexities of the natural world. They provide a structured framework for understanding the behavior and interactions of various physical phenomena. Each law, from the omnipresent force of gravity to the intricate workings of electricity with Ohm’s Law, plays a pivotal role within its respective field, assisting us in navigating the intricacies of nature.
As we continue to probe deeper into the realms of scientific inquiry, we may find that while laws elucidate much about the universe, the beauty of science lies in its ongoing evolution, where each discovery prompts new questions, further expanding our understanding.
Ultimately, the study of scientific laws not only sharpens our intellect but also nurtures a profound appreciation for the world around us, highlighting the elegance of nature’s underlying order. Such knowledge empowers individuals and societies to make informed decisions that shape the trajectory of our future.