Understanding Permanently Incapacitated: A Dual Perspective
The term “permanently incapacitated” emerges at the intersection of legal and medical discourses. It encapsulates not only medical conditions but also profound ethical dilemmas, legal ramifications, and societal implications. This exploration unravels the intricacies of being permanently incapacitated, emphasizing the nuances that practitioners, families, and legal entities must navigate.
Defining Permanently Incapacitated
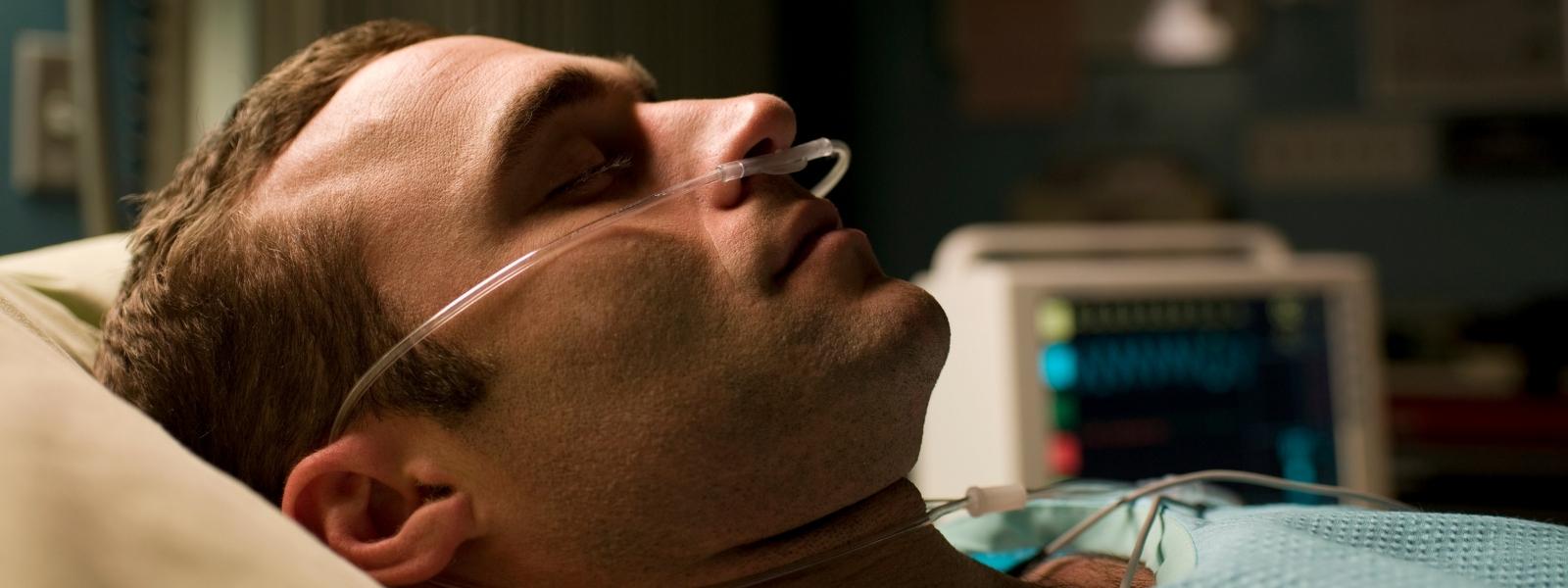
Permanently incapacitated is often defined within both medical and legal frameworks. At its core, it refers to a condition wherein an individual cannot perform essential activities of daily living due to severe impairment of mind or body. In the medical context, this may arise from catastrophic injuries, degenerative diseases, or prolonged illnesses that critically compromise an individual’s cognitive or physical faculties.
From a legal standpoint, the designation of someone as permanently incapacitated has significant ramifications. It implies that the individual is unable to make decisions regarding their own healthcare, finances, or personal affairs. This state triggers the need for guardianship or conservatorships, where legal representatives are appointed to act in the best interests of the incapacitated person.
Medical Context: Conditions Leading to Permanent Incapacitation
Various medical conditions can lead to a classification of permanent incapacity. These include:
- Traumatic Brain Injuries (TBIs): Sustaining a TBI can severely impact cognitive functions. Individuals may experience disruptions in memory, problem-solving, and even personality changes, culminating in a permanence that alters their previous lifestyle.
- Neurological Disorders: Conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease or Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) progressively deteriorate an individual’s cognitive and physical capacities, leading to irreversible decline.
- Severe Stroke: A major stroke can result in profound impairment, affecting movement and speech, often requiring lifelong care or assistance.
- Coma or Vegetative States: Individuals in these states may never regain consciousness or cognitive awareness, necessitating long-term care and decision-making by legal proxies.
Understanding these conditions and their effects provides indispensable context for evaluating what “permanently incapacitated” signifies in practical terms.
Legal Implications of Permanent Incapacity
In the legal sphere, declaring someone as permanently incapacitated is a momentous decision. It involves comprehensive evaluations conducted by medical professionals to corroborate the extent of an individual’s impairments. The legal process typically entails assessing whether the individual can make informed decisions regarding personal health, finances, or legal matters.
Guardianship plays a pivotal role here. When a court determines that an individual is permanently incapacitated, it often assigns a guardian—an individual or institution that takes on the responsibility of making decisions for the incapacitated person. This role encompasses a spectrum of duties, ranging from healthcare decisions to managing finances. Guardianship effectively alters the dynamics of autonomy and decision-making, underscoring the weight of this designation.
Ethical Considerations in Determining Incapacity
The complexity of permanently incapacitated status raises ethical inquiries. How does society define and conclude incapacity? What measures are in place to protect vulnerable individuals from exploitation? The intersection of guardianship laws and medical assessments highlights the delicate balance between autonomy and protection.
Furthermore, ethical dilemmas are pronounced when an individual’s wishes, expressed prior to their incapacity, are in contradiction with the actions taken by guardians or legal representatives. In an era where personal autonomy is highly valued, the notion of encroaching upon an individual’s right to make decisions—even if they may seem impaired—elicits significant ethical discourse.
The Societal Impact of Permanent Incapacity
The ramifications of being deemed permanently incapacitated extend beyond individuals and their guardianship arrangements; they reverberate throughout society. Families bear emotional and financial burdens. Caring for a permanently incapacitated family member can strain relationships, drain resources, and lead to chronic stress.
Additionally, the legal and healthcare systems must grapple with the institutional implications of allocating resources toward permanently incapacitated individuals. Funding for long-term care facilities, specialized medical treatments, and rehabilitation services becomes pivotal in addressing the needs of this demographic. Society must question how it prioritizes care for the incapacitated and the ethical implications of such decisions.
Supporting Those Who Are Permanently Incapacitated
For individuals and families affected by permanent incapacity, support structures must be established. Initiatives such as community outreach programs, healthcare services, and legal assistance can significantly ameliorate the challenges faced. Educational campaigns aimed at fostering understanding about the conditions leading to permanent incapacity and the associated legal ramifications can empower families and communities.
The creation of advanced care planning documents, such as living wills and durable powers of attorney, provides an essential mechanism for individuals to express their preferences and designate trusted individuals to make decisions on their behalf long before any incapacity arises. This proactive approach can alleviate some of the burdens imposed on families during a crisis.
Conclusion
The concept of being permanently incapacitated is laden with complexity, encompassing profound medical, legal, and ethical dimensions. To grasp its full implications, it is essential to consider the myriad factors that contribute to this state and its consequences on individuals and society. As we endeavor to create more supportive environments, understanding the dynamics of permanent incapacity can aid in fostering compassionate, informed responses to those impacted by this challenging circumstance.