Imagine standing on a sprawling plain, the wind whispering through the grass while the sun casts a warm glow over the landscape. As you ponder this idyllic scene, a question arises: what if this environment could provide sustainable energy for generations to come? Welcome to the world of renewable resources — a realm where nature plays an essential role in addressing the pressing challenges of energy consumption and environmental conservation.
At its core, a renewable resource is a natural resource that can replenish itself over time, making it fundamentally different from finite resources like fossil fuels that may deplete with overuse. In this exploration, we will delve into notable examples of such resources, their implications, and the intricate balance needed to utilize them effectively.
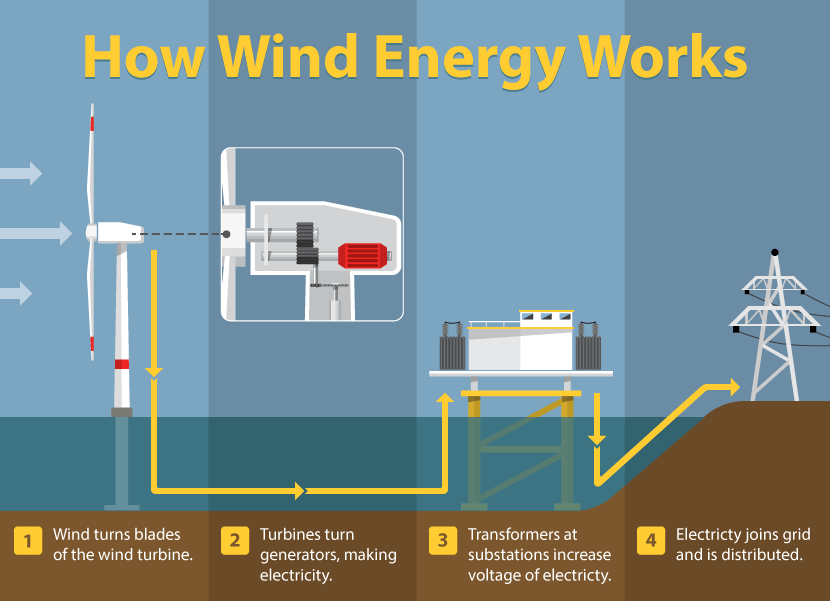
One of the most prominent examples of a renewable resource is wind energy. Harnessed through a marvel of engineering — the wind turbine — this renewable energy has gained traction as one of the cleanest forms of power generation. Wind turbines capture the kinetic energy of wind and convert it into electricity, providing a sustainable solution to our growing energy needs. Yet, here lies the challenge: how can we ensure that the locations for these wind farms are both efficient and minimally disruptive to wildlife and natural landscapes?
Consider solar energy as another formidable contender in the renewable resource arena. Solar panels, placed strategically on rooftops or sprawling solar farms, convert sunlight into usable energy. With the potential to provide clean, sustainable power almost everywhere on the planet, solar energy shines bright. However, the challenge persists: can we optimize energy storage solutions to manage instances when the sun doesn’t shine? As we accumulate more solar energy, the need for innovative storage technologies becomes paramount to harness this resource effectively.
Now, let us turn our gaze towards hydroelectric energy — a resource that utilizes the flow of water to generate power. Through the construction of dams and hydroelectric plants, vast quantities of water are transformed into electricity, powering cities and homes alike. However, this method presents its own set of adversities, such as the ecological impact of altering river ecosystems and the displacement of communities. Is it possible to reap the benefits of hydroelectric power while also safeguarding the intricate web of life that thrives in our waterways?
As we explore further, geothermal energy emerges as an intriguing player. Tapping into the Earth’s internal heat, geothermal plants harness steam and hot water to create electricity. This resource boasts an impressive efficiency compared to other renewable technologies, but the challenge lies in location; suitable geothermal sites are not ubiquitous. How can we expand our geographical horizons to exploit this potent resource without negatively impacting the environment around these plants?
Biomass, encompassing organic materials ranging from plant matter to animal waste, represents yet another renewable resource. When utilized correctly, biomass can be converted into energy through various processes, including combustion or anaerobic digestion, creating electricity or fuel. However, here we encounter a conundrum: in an effort to secure energy, will we contribute to deforestation or disrupt local food supply chains? Striking the right balance is crucial to ensuring that biomass remains a sustainable option moving forward.
Next, we must address the role of tidal and wave energy as less conventional yet equally promising renewable resources. These harness the natural movements of oceans and seas, capturing energy from tides and waves in much the same way as wind turbines capture the air. The potential is profound, but coastal communities must grapple with the potential disruption of marine ecosystems. Can we innovate these technologies while rendering our oceans a sanctuary for marine life?
As we consider the aforementioned renewable resources, it is imperative to remember that each has its own unique advantages and challenges. The quest for sustainability is fraught with obstacles, yet it is a pursuit that we must fervently undertake. It compels us to be thoughtful about how we approach energy consumption, harnessing the power of nature while mitigating detrimental effects on the environment.
Collaboration between governments, industries, and communities will be paramount in overcoming these challenges and advancing renewable resources. This synergy will yield innovative solutions that enhance efficiency, reduce emissions, and secure a sustainable future for all. Furthermore, consumer education and awareness can play key roles in encouraging the adoption of renewable technologies, thus ensuring that the demand for cleaner options continues to grow.
What might the future look like if we fully embrace renewable resources and commit to their integration into our daily lives? It could usher in a new era of energy that is sustainable, equitable, and diverse. As each challenge is addressed, the synergy of technology, policy, and community involvement can pave the way for a future that not only embraces renewable sources but makes them the cornerstone of our energy landscape.
In conclusion, renewable resources stand as a beacon of hope in our efforts to achieve sustainable energy solutions. They invite us to reflect on our relationship with the environment and challenge us to innovate responsibly. As we continue to explore the depths of these renewable resources, the question should not be whether we can harness them effectively, but rather how can we do so while nurturing the planet that has nurtured us for so long?