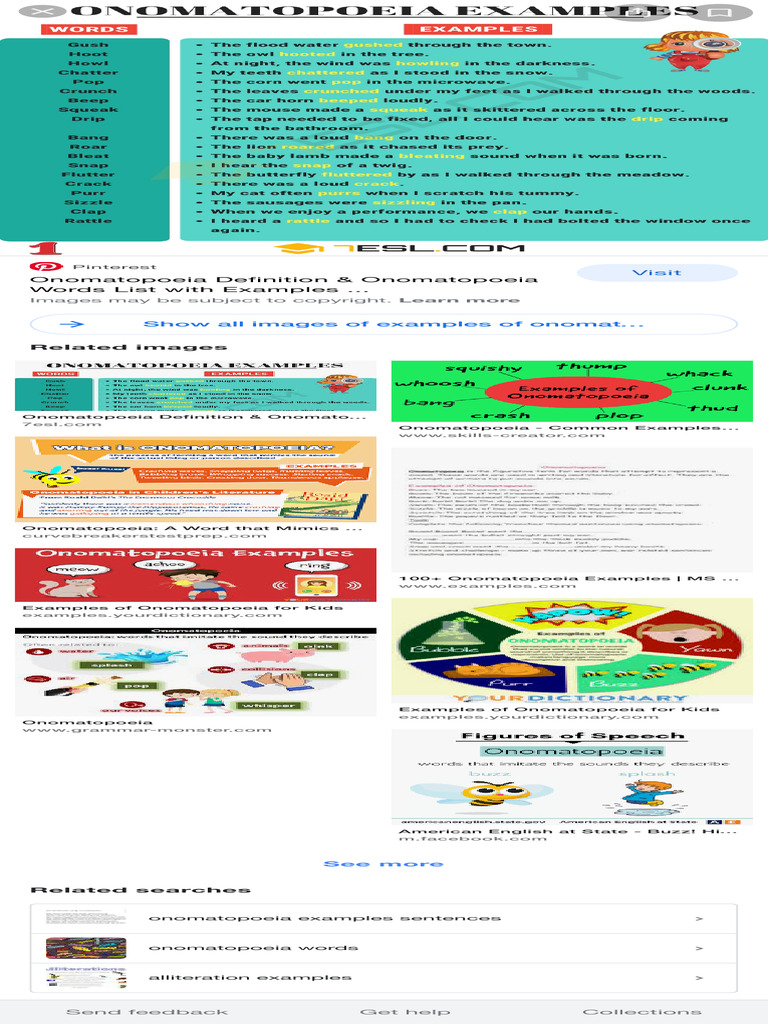
Onomatopoeia, an evocative linguistic device, showcases the richness of language in a uniquely auditory fashion. It is the phenomenon where word formation mimics the sounds associated with the objects or actions they refer to. Essentially, this linguistic tool bridges the auditory and visual worlds, promising a shift in perspective and compelling readers to engage more deeply with text. Let’s delve into various facets of onomatopoeia, illustrating its significance, applications, and the cognitive shifts it inspires.
Understanding Onomatopoeia
Onomatopoeia is derived from the Greek words “onoma,” meaning name, and “poiein,” meaning to make. This delightful juxtaposition characterizes the interplay between sound and meaning, whereby words like “buzz,” “bang,” and “murmur” evoke specific auditory images. These words are not just mere descriptors; they encapsulate experiences, emotions, and memories, adding a tactile dimension to language. The presence of onomatopoeia can elevate prose, transforming simple narratives into vivid, sensory experiences.
Historical Context
The origins of onomatopoeia can be traced back to ancient languages, where the need to convey sound was imperative to storytelling. Epic poets, for instance, exploited this device to enhance listening experiences, whereby the sound of a word resonated with its meaning, engaging audiences more fully. Cultures across the globe have developed their own forms of onomatopoeic words, reflecting the sounds of their environments. For example, the English “roar” for a lion is paralleled in many languages, demonstrating a shared human experience and a universally resonant comprehension of sound.
The Role of Onomatopoeia in Literature
A hallmark of creative writing, onomatopoeia weaves its way through poetry, prose, and even song lyrics, creating a symphony of sounds that enriches the text. Imagine a literary scene where raindrops are described as “pitter-patter”; the phrase transports the reader to a serene setting, allowing them to visualize and hear the natural rhythm of falling rain. In poetry, such auditory imagery summons emotional responses, compelling readers to feel the weight of words rather than just read them.
Onomatopoeia in Various Genres
Different literary genres leverage onomatopoeia to serve distinct purposes. In children’s literature, it acts as a playful tool to capture young readers’ attention. Words like “splash,” “zoom,” and “pop” not only entertain but also facilitate language acquisition by associating sounds with their meanings. In contrast, in horror narratives, authors might employ harsher sounds like “cackle” or “howl” to evoke fear and unease, effectively deepening the atmosphere of dread.
Everyday Language and Communication
Beyond literature, onomatopoeia permeates everyday communication. From the sounds of nature to the cacophony of urban life, these words reflect our interactions with the world. Phrases like “clang,” “crash,” and “whirr” succinctly describe phenomena that can be otherwise cumbersome to articulate. In this way, onomatopoeia serves as an efficient communicative tool, fostering clarity and enhancing expressiveness.
Psychological Impact
The allure of onomatopoeia extends into the cognitive domain, influencing how we process and remember language. Studies have shown that words evocative of sound often elicit stronger emotional responses, enhancing memory retention. When individuals encounter onomatopoeic words, their brains stimulate sensory responses linked to those sounds, creating an immersive experience. This psychological engagement transforms passive reading into active, almost visceral participation, enriching comprehension and retention.
Applications Beyond Literature
In contemporary society, the influence of onomatopoeia has transcended literature, sprawling into advertising, branding, and even gaming. Advertisers adeptly harness onomatopoeia to create catchy slogans that resonate with consumers on an instinctual level. Think of iconic campaigns that employ phrases like “crunch” or “sizzle,” embedding themselves within our collective consciousness. In gaming, sound effects like “boom” and “zap” enhance the immersive universe players inhabit, making experiences more engaging and dynamic. This versatility illustrates how onomatopoeia serves as a bridge between art and commerce.
Exploring Cultural Variants
Onomatopoeia is not monolithic; it varies across cultures and languages. Each language possesses unique examples that might not have direct translations. For instance, the English “cock-a-doodle-doo” for a rooster differs from the French “cocorico.” These variations reflect cultural nuances, revealing how different societies interpret and articulate their auditory environments. This exploration can foster cross-cultural understanding and appreciation of linguistic diversity.
The Future of Onomatopoeia
As language evolves, so too does the function of onomatopoeia. The digital age has introduced new sounds that demand innovative expressions. With the rise of social media, emojis and sound bites have created a contemporary lexicon that borrows from traditional onomatopoeic principles. Words and phrases morph, adapting to modern communication while retaining their essence of imitative sound. This evolution invites curiosity, encouraging exploration into how we perceive and articulate sound in an ever-changing world.
In conclusion, onomatopoeia is more than a mere literary tool; it is an experiential catalyst. By catapulting us into vivid auditory realms, it reshapes our understanding of language. Whether in childhood tales or contemporary media, the allure of sound-infused words weaves a captivating tapestry that enhances our comprehension and emotional engagement. Embracing onomatopoeia not only enriches our vocabulary but also invites us to experience language in a profoundly transformative way. Let your curiosity guide you to discover the symphony of sounds awaiting within the words you encounter every day.