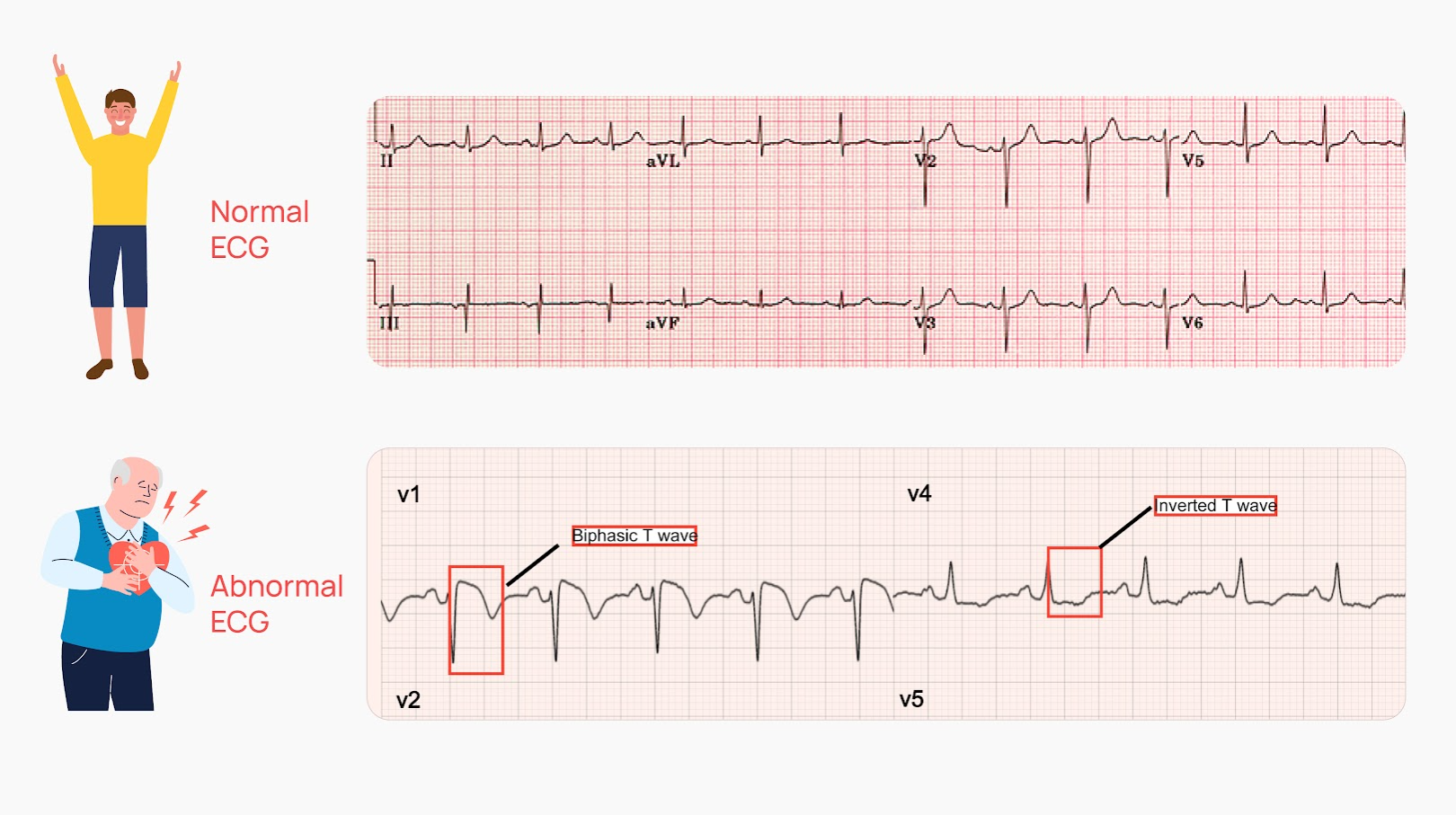
Understanding the results of an electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) can often seem daunting to patients. This vital test captures the electrical activity of the heart, providing crucial insights into cardiovascular health. While a normal ECG signifies a well-functioning heart, an abnormal result may hint at various health complexities that warrant further investigation. In this article, we delve into what an abnormal ECG signifies, the different types of abnormalities, and why a deeper understanding is essential for patient empowerment.
1. The Basics of ECG Interpretation
Before diving into abnormal results, it’s imperative to grasp the mechanics of an ECG. This test records the heart’s electrical impulses and presents them as waves on a graph. Various segments of the ECG correspond to specific phases of the heartbeat, including:
- PR Interval: Reflects the time it takes for electrical signals to travel from the atria to the ventricles.
- QRS Complex: Indicates ventricular depolarization, depicting when the ventricles contract.
- ST Segment: Represents the period between ventricular depolarization and repolarization.
- QT Interval: Measures the time taken for the heart to contract and then recover.
Each component is pivotal, and deviations from the norm may suggest various medical conditions.
2. Types of Abnormal ECG Findings
Several categories of abnormalities can manifest on an ECG. Here are some critical types to consider:
a. Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia refers to an irregular heartbeat, which can include tachycardia (a rapid heartbeat), bradycardia (a slow heartbeat), or even uncoordinated rhythms. These anomalies may signify issues such as electrolyte imbalances, heart disease, or damage from a previous heart attack. Detection of arrhythmias is paramount, as they can lead to serious complications, including stroke or heart failure.
b. Ischemic Changes
Ischemic changes indicate that a portion of the heart muscle is not receiving adequate blood flow, often due to blockage in the coronary arteries. This is visually represented through elevated ST segments or newly formed Q waves on the ECG, suggesting possible myocardial infarction (heart attack). Timely identification of ischemic changes can be lifesaving, allowing for interventions that restore blood flow.
c. Ventricular Hypertrophy
Ventricular hypertrophy occurs when the heart’s ventricles become enlarged, potentially due to chronic high blood pressure or heart valve disease. ECG findings associated with this condition may show increased voltage in the QRS complex. Recognizing ventricular hypertrophy is vital for managing underlying conditions and preventing further cardiac complications.
d. Conduction Abnormalities
These abnormalities occur when electrical impulses are blocked or delayed as they travel through the heart’s conduction pathways. A bundle branch block, for example, may be detected when one of the major pathways is impeded. Although some individuals may exhibit conduction blocks without symptoms, they can pose risks, particularly if they lead to more critical conditions like complete heart block.
3. Causes of Abnormal ECG Results
Several factors can contribute to abnormal ECG findings. These include:
- Heart Conditions: Various underlying heart issues such as cardiomyopathy, heart valve diseases, and congenital heart disorders.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Abnormal levels of potassium, calcium, or magnesium can significantly affect heart stability.
- Medications: Certain drugs can alter heart rhythms or conduction pathways, reflecting abnormal patterns on an ECG.
- Physical Stress: High levels of physical exertion or mental stress can temporarily alter heart rhythms.
Understanding these factors assists healthcare professionals in pinpointing the cause of abnormalities, enabling them to devise effective treatment plans.
4. Next Steps After Receiving Abnormal Results
Receiving abnormal ECG results can understandably induce anxiety. However, it is crucial to approach the next steps with a level head. Here’s what typically follows:
a. Further Testing
To gain a comprehensive understanding of the heart’s health, physicians may recommend additional testing, such as echocardiograms, stress tests, or Holter monitoring. These tests can provide deeper insights into structural issues and functional capacity.
b. Lifestyle Modifications
Depending on the underlying cause, patients may be encouraged to adopt lifestyle modifications. This can include dietary changes, exercise regimens, and stress management techniques—all of which contribute to enhanced cardiovascular health.
c. Medical Management
In some cases, medication may be warranted to manage arrhythmias, control blood pressure, or address other underlying conditions. It’s crucial to adhere to the prescribed regimen and communicate any side effects to your healthcare provider.
5. The Importance of Early Detection
Ultimately, early detection and appropriate management of abnormal ECG findings play a pivotal role in preventing more severe cardiovascular events. Regular check-ups, particularly for those with risk factors, can lead to timely interventions that improve heart health and overall well-being. Remember, your heart health is invaluable, and being proactive can lead to a more prosperous life.
In conclusion, while abnormal ECG results may seem alarming, they serve as essential indicators of heart health. By understanding what these abnormalities signify and the implications for treatment, individuals can take proactive steps toward a healthier future.