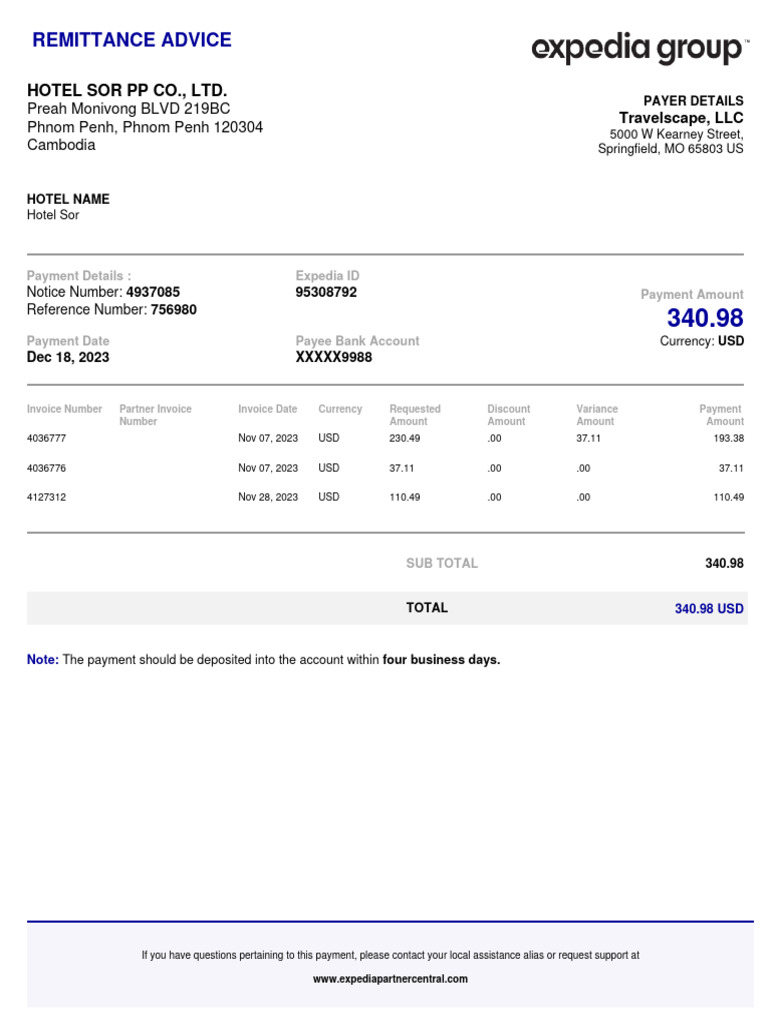
In the intricate world of financial transactions, remittance plays a pivotal role akin to an invisible thread weaving together disparate economies. Just as a message in a bottle finds its way from one shore to another, remittances traverse borders, knitting together families and communities separated by miles. At the heart of this multifaceted process lies the remittance address, an essential yet often misunderstood component that serves as the destination for these monetary travels. Understanding what a remittance address means and how it functions can illuminate some of the more obscure corners of payment instructions.
A remittance address can be defined as the specific location or account where a payment is directed, a literal and figurative waypoint for money. This address often includes various elements such as bank account numbers, physical addresses, or even digital currency identifiers. Imagine a treasure map—the remittance address is where the ‘X’ marks the spot, guiding the sender to ensure that their funds reach the intended recipient without detours through unwanted paths.
The significance of accurately designating a remittance address cannot be overstated. Just as a misplaced letter might never reach its recipient, an inaccurately specified remittance address can lead to financial confusion, delays, or even complete losses. When the sender embarks on the journey of transferring funds, any error along the way can turn a seamless transaction into a daunting ordeal, akin to a ship sailing off course due to a miscalculated heading.
To delve deeper, let’s decode the components that comprise the remittance address in the realm of modern payment systems. Firstly, it is essential to understand the various types of remittances—domestic and international. For domestic transfers, a simple bank account number may be sufficient, forming a quaint direct line from one account to another within a singular financial ecosystem. Here, the bank serves as both postmaster and gatekeeper, ensuring the funds are delivered accurately and promptly.
On the other hand, international remittances introduce an additional layer of complexity. Just as different countries speak varied languages, financial institutions around the globe employ diverse systems for facilitating transfers. In these cases, a remittance address may include an IBAN (International Bank Account Number), SWIFT code, or even references to intermediary banks that serve as conduits between sender and recipient. These codes act as linguistic keys, unlocking the door to a network of global finance.
Beyond the basic structural components of a remittance address, it is prudent to consider the context in which these addresses are used. The contemporary fascination with digital wallets and cryptocurrency has revolutionized the remittance landscape. In such scenarios, the remittance address morphs into a virtual identifier, a cryptographic alphanumeric string that serves as the destination for digital currency. This transformation echoes the very essence of evolution in communication—from handwritten letters to instant messages—reflecting society’s constant quest for efficiency and immediacy.
Payment instructions tied to remittance addresses further enrich this narrative. Clarity in these instructions is akin to conveying specific directives in a merchant’s ledger. For a successful transaction, senders must include relevant information, often manifesting as a memo or reference code. These details not only assist in tracking the transaction but also serve to inform the recipient about the purpose of the funds. Whether it is for support in times of need, such as covering medical expenses, or simply sending birthday wishes, these nuances paint a vivid picture of the transaction’s intent.
As we navigate the intricacies of remittance addresses, it’s essential to recognize the implications of technological advancements. Emerging fintech solutions have overtaken traditional methods, providing users with an array of payment options that prioritize speed, cost, and security. Mobile applications, blockchain technology, and peer-to-peer transfer systems have fundamentally altered how remittances are dispatched. In this evolving landscape, remittance addresses adapt, ensuring that the very concept of location is redefined in our digital age.
Moreover, the role of regulations and compliance cannot be overlooked. Much like a regulatory honeycomb intricately structured to promote safety and trust, remittance addresses are subjected to local, national, and international laws. Anti-money laundering measures and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations demand accurate and transparent information, making the precision of the remittance address even more critical. This aspect emphasizes not only the monetary transaction but also the ethical responsibility that accompanies it.
As we draw this exploration to a close, one cannot help but appreciate the poetic choreography involved in remittances. The remittance address stands as a beacon, guiding the flow of funds across oceans and continents, bringing joys and alleviating burdens. It is much more than a mere destination; it is the lifeline connecting dreams and realities in an interconnected world.
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of what a remittance address means allows one to navigate the complexities of payments proficiently. Through vivid exploration of its components, implications, and evolving nature in a digital context, we see that remittance addresses are vital in ensuring the seamless transfer of resources worldwide, akin to the lifeblood that nourishes relationships within our global community. By grasping this essential concept, individuals and businesses alike can embark upon their financial journeys with confidence and clarity.